Projects, Scans and Models¶
A project encompasses all 3D data obtained by scanning and postprocessing that can be saved to disk and accessed for later use. In addition, it contains command history and measurement results. For each project, a corresponding folder contains all project data and an A3D project file.
Note
Please note that, the project data is stored as .sst files for versions 16 and above, and may not be accessible.
Artec Studio can display project statistics. It includes information on number of scans, surfaces (frames), polygons, vertices and UV coordinates.
To access this data, call a right-click menu for any Workspace object and select Project info.
If you want to collate data on the selected scans with the total numbers for the project, first mark the required scans using with the  flag.
flag.
Creating a Project¶
To start a new project, select the File → New project menu option. It is a best practice to save this project to a specific folder before you start scanning. If you start scanning with the Save scans directly to disk option enabled or import scans from Ray, a temporary project is created in the Windows temporary folder or another directory if you specified one in Settings.
Saving a Project¶
You can save your project using the File → Save project menu option or by hitting Ctrl + S.
While you’re working with a saved project, the header of the application window displays its full path. Save your project from time to time in the course of processing or otherwise using the scanned material.
Note
Artec Studio saves data incrementally, meaning that if you save an existing project, the application will only save newly changed or added data.
Opening Project and Scans¶
To open an existing project, use the File → Open project menu option or hit Ctrl + O.
Note
Artec Studio versions 16 and above do not support SPROJ files. Projects created with earlier versions in the SPROJ file format, must be converted to the A3D format to be compatible.
By default, when you open a project, the application will restore it to the state in which it was last saved.
Note
When Artec Studio opens a project, it will determine the amount of available memory. If the scan you are trying to load requires more memory than is available in your system, the application will process it as an “unloaded” scan.
Opening an SPROJ file¶
In order to open an SPROJ file in Artec Studio (versions 16 and above), you will need to convert them to the A3D file format. On selecting an SPROJ file to open, Artec Studio will automatically prompt project conversion. Artec Studio will convert the selected project to A3D format and save it separately at the file location you specify. You will not lose your SPROJ project. The converted A3D project will, however, not contain the project’s command history.
Opening a Project from Leo¶
You can obtain projects from Leo via direct connection to the scanner or using an SD card installed in the device.
Connecting to Leo¶
Ensure that your Leo scanner and your computer are connected to the same network and you authenticated using the same credentials
Click File → Import → Leo project (connect to scanner)
Wait for the application to show your Leo scanner. If no device is displayed or you are using a direct connection, follow the steps indented below:
Click Connect by IP
Specify IP address that you may find in Leo network settings
Click Add
Select the required scanner and click Connect
Then using either LMB or ↑ and ↓ select the project that you want to load (Figure 71)
If the selected project contains HD raw data, you can import it by checking Import raw data.
To start HD reconstruction immediately after the import, perform the following actions:
Check Launch HD reconstruction.
Select the desired HD data density in the range from 1× to 64× using the eponymous slider.
The HD data density determines the number of polygons per frame that is used for reconstructing the scanned surfaces from the raw data. With 1× the number of polygons is of the same order as for the SD resolution and 64× corresponds to ~5 million polygons per frame. Increasing the HD data density results in higher degree of resolution, coverage, and detail, but requires more memory and time for the HD reconstruction.
Important
If Artec Studio evaluates your computer’s resources as insufficient for the selected HD data density, then the warning is displayed that the HD reconstruction can take up to several hours on your computer. For information on resources requirements, see the Using HD mode section in System Requirements.
Click Import.
If you have enabled the HD reconstruction, it will start immediately after the data uploading finishes.
Wait for scans to appear in the Workspace panel.
The imported project and scans will be automatically grouped—the group with the project name will be divided into subgroups of scans (see here about grouping). The imported HD scans will have an “HD” mark in their names, for example: Leo HD Scan 1.
If the scans contain information on supporting surface and the corresponding option is enabled in Settings, Artec Studio will also launch base removal.
Note
You can import HD projects from Artec Leo multiple times with different values of HD data density.
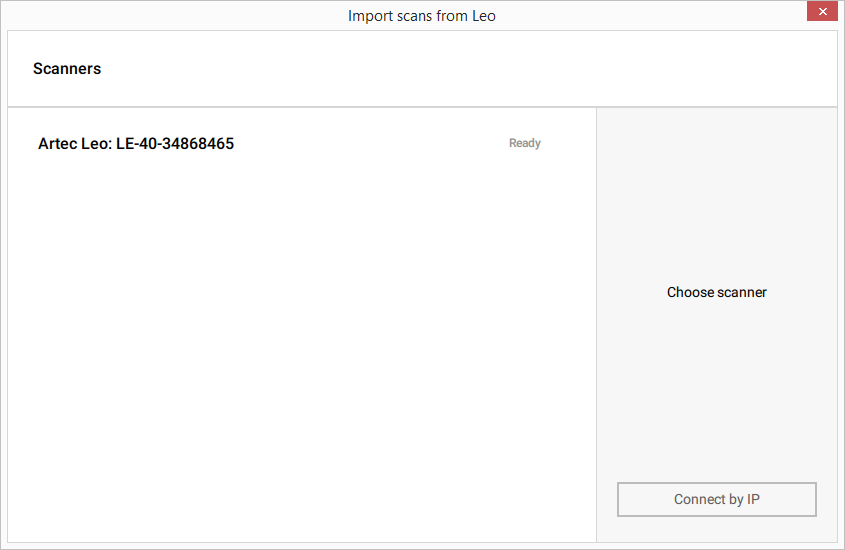
Figure 70 Scanner list and the Connect by IP button.¶
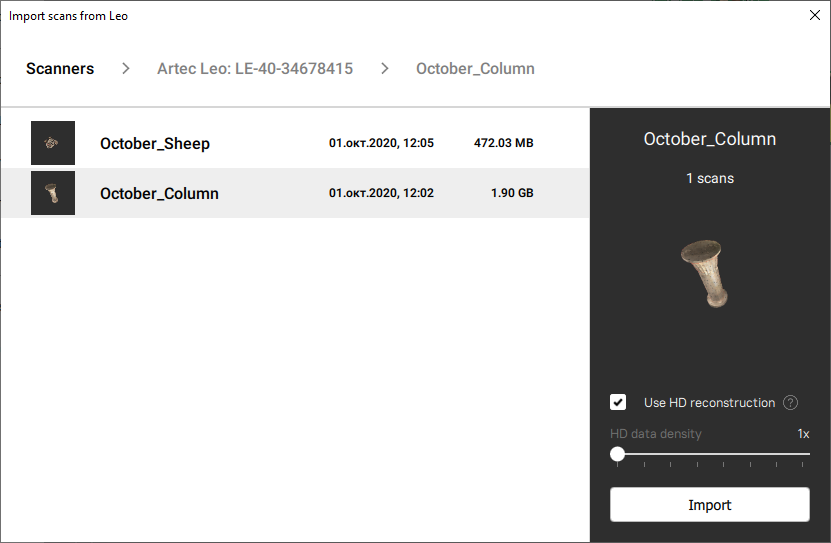
Figure 71 Dialog for selecting Leo projects to import.¶
Using SD Card¶
If you want to open Leo scans without having to connect to the device, use the following method:
On Leo, first copy a project to SD card.
Then insert the card into the computer with installed Artec Studio.
Click File → Import → Leo project
Browse for the required project folder
Select the folder containing Leo project and click Select folder. Import will start.
Note
HD data from Artec Leo can be exported to an SD card with the *.leo format.
Importing Models and Scans¶
Importing is another way to load data into Artec Studio in place of capturing or opening a project. You can import scan files created in earlier versions of the software, individual frames, point cloud data, as well as CAD models in the following formats:
|
Artec 3D scan format |
|
Stanford polygon file format |
|
Stereolithography file format |
|
VRML file; actual extension is |
|
Wavefront OBJ file format |
|
Disney per-face texture mapping format |
|
Artec Ray original point cloud |
|
Artec Ray point cloud |
|
(CAD format) Standard for the Exchange of Product model data |
|
(CAD format) Initial Graphics Exchange Specification |
|
(CAD format) Parasolid XT data format |
Importing Scans, Meshes or Point Clouds¶
To import a file, use the File → Import → Scans, meshes or point clouds menu option or hit Ctrl + I . Next, select a file for importing. You can also drag and drop a file into the main Artec Studio window, or just double click on it.
Note
The import process runs in the background, so you can continue working with the scans you’ve already loaded. The progress indicator for the import operation will appear at the bottom of the main application window. To abort the operation, click Cancel in the bottom-right corner.
Artec Studio will import frame files as individual single-frame scans. After importing each scan, the application calculates the key frames for any scan that contains more than one surface. Also, the application will check the surfaces for defects when the appropriate setting is enabled (see Surface-Consistency Detection During Import). If it finds defects, it will show a dialog with a list of defective surfaces once the import operation is complete. You can then choose which ones should be corrected.
Importing CAD models¶
You can import CAD models created in different CAD programs and saved to the following formats: STEP, STP, IGES, IGS, X_T.
To import a file, use the File → Import → CAD models menu option. Next, select a file for importing. You can also drag and drop a file into the main Artec Studio window, or just double click on it.

Figure 72 Imported CAD model.¶
Exporting Models, Scans and Point Clouds¶
When you want to store data for future processing, the best approach is to save the project as an A3D file or to export the data to the SCAN format. Any Artec Studio version can open the latter format. If you plan to use the data in other applications, however, you should save scans and individual frames in another format.
You may also need to perform one of the following tasks:
Exporting Scans¶
To export scans:
Select the File → Export → Scans command.
Click the … button to open and specify the destination folder.
Select Scan export format using the eponymous dropdown list.
If the selected format supports textures, also specify the texture format.
Select the Apply transformation checkbox, or leave it cleared (for more information, consult Understanding How Artec Studio Applies Transformations).
Click OK.
|
Stanford polygon file format |
|
Stereolithography file format |
|
Wavefront OBJ file format |
|
VRML file; actual extension is |
|
Direct X file format |
|
Artec 3D scan format |
|
Stanford polygon file format with vertex colors, actual extension is |
|
OBC point-cloud file |
Note
The export process for models and scans runs in the background, so the application will allow you to continue working with the scans. The progress indicator for the export operation will appear at the bottom of the main application window. To abort the operation, click Cancel in the bottom-right corner.
Exporting Meshes (Models)¶
You can export a single model (mesh) or several models at a time. Models can be merged before export or exported separately.
To export a mesh or multiple meshes:
Mark one or more models using
 or select frames in the scan by clicking on them while holding the Ctrl key.
or select frames in the scan by clicking on them while holding the Ctrl key.Select the File → Export → Meshes command. A dialog window will appear (Figure 73).
Tip
Ctrl+Shift+E hot key does the same.
Click … and specify the destination folder.
Use one of the following options for the file names:
Leave the field blank and the exported meshes will get the same names as their corresponding models in the Workspace panel.
Enter a custom export name. If you are going to export multiple meshes, this name will be used as a mask. For example, if you specify ‘Model’ as the custom export name, then the meshes will be named as Model1, Model2, and so on.
Select an appropriate mesh format from the Model export format dropdown list 1 (see the description of available formats below).
If the model has texture and the selected mesh format supports it, choose an appropriate texture export format from the eponymous dropdown list (see Storing and Exporting Color Information for details).
To merge the models into a single mesh before exporting, select the Merge models checkbox. Otherwise, each model selected in the Workspace panel will be exported to a separate file.
To move the models to origin before exporting, select the Move to origin checkbox.
Click OK.
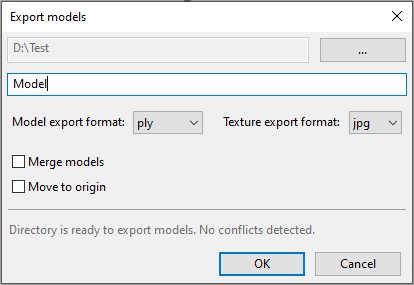
Figure 73 Dialog for exporting meshes.¶
|
Stanford polygon file format (standard and with the support for vertex color) |
|
Stereolithography file format |
|
VRML file (1.0 and 2.0); actual extension is |
|
Wavefront OBJ file format |
|
Point cloud 3D format |
|
American Academy of Orthotists and Prosthetists file format |
|
Walt Disney Ptex: mesh with per-face texture mapping |
|
Direct X file format (binary and text) |
|
XYZRGB file format |
|
ASTM E57 3D file format |
- 1
If you type an extension in the file name field, application will use it rather than the selected mesh file format.
See also
Exporting CAD objects¶
You can export CAD primitives created in Artec Studio to the following formats: STEP, IGES, X_T.
To export CAD primitives:
Exporting Point Clouds¶
You can export point-cloud scans obtained from Ray scanner to either of the following formats (respective units are given in the third column):
|
Leica Geosystems Cyclone Point Cloud. |
Meter |
|
XYZRGB file format |
Specified in settings |
|
Artec Ray point cloud; various versions (v2, v3, v5, v6). |
Micron |
Mark one or more point-cloud scans using
 flag in Workspace. Ensure that you have selected a point-cloud scan by double-clicking its name: the panel must show point-cloud properties.
flag in Workspace. Ensure that you have selected a point-cloud scan by double-clicking its name: the panel must show point-cloud properties.Select File → Export → Point clouds.
Specify the destination folder and required format and click Save.
Merging Sections¶
When exporting to PTX, ensure the Export point clouds to PTX with merged sections checkbox is marked in the Artec Studio settings. This option merges all sections (selections made during scan with Ray scanner) so that third-party software products can open the exported file.
Understanding How Artec Studio Applies Transformations¶
Artec Studio offers two options for exporting surfaces:
Store surfaces using the scanner coordinates and create
XFtext files that contain the coordinates calculated during registration. To use this approach, clear the Apply transformations checkbox.Store surfaces that are relocated to the positions calculated during registration. In this case,
XFfiles contain no relevant data. To use this approach, select the Apply transformations checkbox.
Special Aspects of Scan Placement¶
In most cases when you’re exporting a scan to a common 3D-graphics format, you should select the Apply transformations checkbox. By doing so, you instruct third-party applications to display surfaces in the same way that Artec Studio does: that is, with the origin at the center of mass. If for some reason you need to store a scan in the scanner’s coordinate system—in other words, with surfaces located at a distance from the origin that is equal to scanner’s operating range—clear the Apply transformations checkbox.
Technically, Artec Studio saves scans in the scanner’s coordinate system, but it displays them in a user-friendly manner by placing the origin at the center of mass. The actual positions of surfaces calculated during registration are stored in text (XF) files. Therefore, when you’re importing files using Artec Studio, it makes no difference whether the checkbox was cleared when Artec Studio exported them. It does make a difference, however, for third-party applications that cannot read XF files simultaneously with 3D geometry.
Storing and Exporting Color Information¶
You can transfer color information for 3D surfaces in three ways. The most common is through a texture using a separate bitmap file (see Applying Texture (Procedure)). Another option is to save color information in each vertex of a mesh. The third is to assign a small textured fragment to each polygon. The two latter methods produce no texture files.
Colors stored in a vertex are blended throughout the polygon. As a result, you should avoid oversimplifying the exported mesh; otherwise, colors blended over a large face may fail to render true texture information.
Texture stored as a bitmap |
|
|---|---|
Model file contains separate texture for each face |
|
Formats that support vertex color |
|
When exporting texture as a bitmap image, you can select one of the following formats: PNG, BMP or JPG. PNG format provides the best quality for a given file size thanks to its lossless image compression. JPG is the most compact format.
Exporting Target Coordinates¶
If you scan while in the Targets tracking mode using only Artec scanners, you can save an OBC file containing the target coordinates. Once you finish scanning, run Global registration, then do the following:
Use the
 button to mark any scans that you captured without having uploaded an
button to mark any scans that you captured without having uploaded an OBCfile.Select the File → Export → Scans command.
Click the … button to open and specify the destination folder.
Select obc from the Scan export format dropdown list.
Click OK. The
targets.obcfile will appear in the folder you specified.
For more information on the OBC file structure, consult the FAQ.
Exporting to Leios¶
Artec Studio enables you to export files to Leios by accessing the File menu if the Leios software is already installed on your computer.
Select a model in the Workspace panel
Open File → Export to Leios
Then, in Leios, select millimeters as the length unit for the imported files.
Exporting to Geomagic Design X¶
Polygonal models created in Artec Studio are insufficient for most design needs. Geomagic Design X (formerly Rapidform XOR) is purpose built to create manufacturing-ready CAD models directly from meshes.
To export a model,
Make sure Geomagic Design X is installed on your computer
Select the Export to Design X command from the File menu
Wait for the model in
OBJformat to open in the reverse-engineering system.
Figure 74 Model exported to Geomagic Design X¶
Exporting to SolidWorks¶
Artec Studio allows you to export models, CAD primitives and cross-sections to SolidWorks. You can export CAD primitives and cross-sections directly to SolidWorks without any third-party plug-ins. However, to export models, you require the plug-in Geomagic for SolidWorks.
To export models or primitives,
Make sure SolidWorks is installed on your computer
For models, make sure the plug-in is also installed on your computer
In the Workspace panel, mark one model or object using the
 flag
flagSelect the Export to SolidWorks command from the File menu
Wait for the selected model or object to open in the CAD system.
Exporting to Control X¶
Control X is a 3D quality control and dimensional inspection software with which you can capture and process the data from 3D scanners to measure and inspect quality. With Artec Studio 16 you can export models to Control X, or directly inspect them and generate inspection results.
To inspect a model in Control X,
Make sure Control X is installed on your computer
In the Workspace panel, right-click on the model that you want to inspect
Select the Inspect in Control X option from the dropdown menu
Wait for the model to open in Control X and generate the inspection report
History of Project Changes¶
Artec Studio stores all data changes, and you can later undo any unnecessary changes.
You can see the saved changes and their use of memory in the History panel.
To open the panel, click the  button at the bottom left or hit Ctrl+H
button at the bottom left or hit Ctrl+H
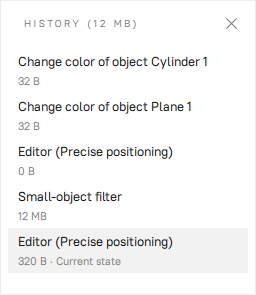
Figure 75 The History panel.¶
Click on the desired operations in the list to undo or redo them. Operations can be undone (redone) only sequentially, i.e. you cannot skip any of them selectively.
To quickly undo or redo the changes stored in the project history, you can also use the following options:
Undo:
Redo:
When you save a project, Artec Studio stores 3D data together with the history of changes. You cannot limit the maximum length of command history. The Clear command history button clears the command history, and thus frees up RAM, and makes the undo operation for the most recent changes unavailable. Additionally, in the Clear History window, you can choose to Keep the last’n’ actions, and clear the rest. Simply specify the number of actions you would like to keep, and confirm. To clear the history, you can use the Edit → Clear history menu option in the main window or hit Ctrl+Alt+H.
Autosaving a Project¶
Artec Studio 16, by default autosaves projects and changes made to projects instantaneously. A newly created and yet manually unsaved project is automatically saved and stored in the Temporary folder (see Temporary Folder). You can manually save the project in a preferred location later or access it from the temporary folder as necessary.

