Viewing Scans and Models¶
Choosing Projections¶
The View menu allows you to choose between perspective and orthogonal projections when displaying the model in the 3D View window.
Perspective view is the central projection on a plane produced by direct rays that focus on one point: the projection center. This method produces a visual effect similar to human eyesight.
Orthogonal view is when the projection center resides infinitely far from the plane of projection; in this case, the projection rays are perpendicular to the observation plane. This method preserves parallel lines and is more commonly used for measurement (see Measurement Tools for details).
You can also change projection type in other ways:
- Hit Ctrl + 5 on the main keyboard
- Hit 5 on the extended numeric keypad (numpad)
Viewpoints¶
To quickly toggle a camera view between several predefined positions, use navigation cube, View menu or the keyboard combinations listed in Table 7.
In comparison with the other ways, navigation cube provides more flexibility in orienting objects in the window. Apart from using labeled faces (TOP, FRONT, LEFT, etc.), cube allows one to orient scene to intermediate positions with the help of controls located on the edges and vertices (see Figure 69).
| Viewpoint | Keyboard | Extended Numpad |
|---|---|---|
| Front | Ctrl + Shift + 1 | 1 |
| Back | Ctrl + 1 | Ctrl + 1 |
| Right | Ctrl + Shift + 3 | 3 |
| Left | Ctrl + 3 | Ctrl + 3 |
| Top | Ctrl + Shift + 7 | 7 |
| Bottom | Ctrl + 7 | Ctrl + 7 |
The Home command of the View menu or H keystroke restores the view to its original position.
The Fit to view menu option,  button or F keystroke automatically fits the object to the 3D View window.
button or F keystroke automatically fits the object to the 3D View window.
For point-clouds, you can have a look at scan from the Ray perspective. Open the right-click menu for this scan and select the Go to scanner viewpoint command to this end.
Displaying 3D Data¶
The toolbar on the right of the 3D View window features controls for data-display modes. If minimized, it can be opened by clicking button  in the 3D View window (see Figure 70). All the commands for viewing and switching between modes are also available in the View menu.
in the 3D View window (see Figure 70). All the commands for viewing and switching between modes are also available in the View menu.
Rendering and Shading Modes¶
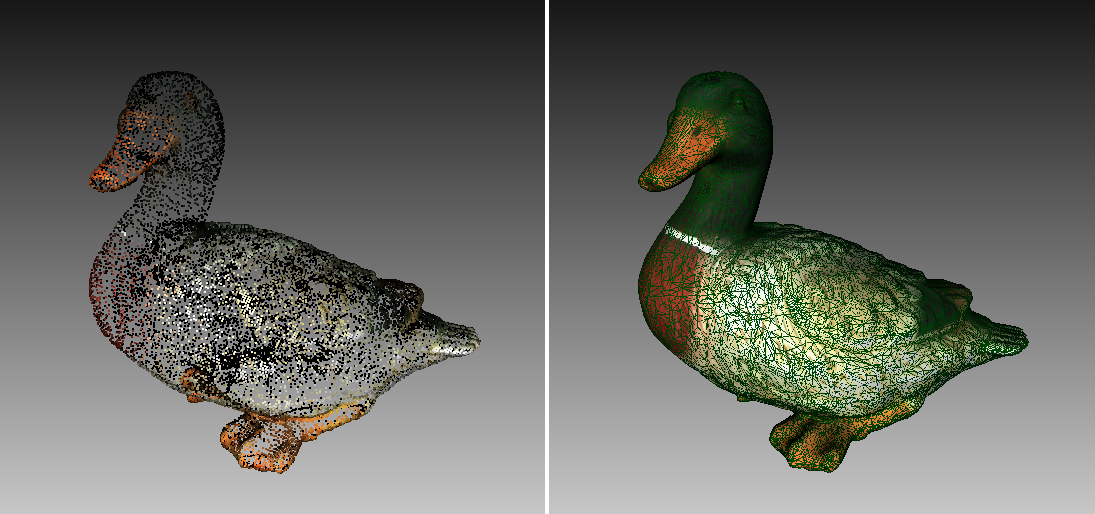
Figure 71 Examples of model using different rendering modes.
Both the View menu and the 3D View toolbar allow you to choose one of the following 3D rendering options for scanned frames:
- Render solid
- the most common way to render with a solid fill on all faces using your selected shading method
- Render wireframe
- display polygonal-mesh edges without applying a solid fill to the faces
- Render points
- display polygonal-mesh vertices
- Render wireframe over solid
- apply a solid fill to the faces and use a different color to display edges. This method enables you to visually assess the quality of the polygonal model (see Mesh Simplification for details).
- Render points and solid
- automatically display scans in point view, but display models in solid-fill view. This mode eliminates the need to switch to another mode in order to find the best rendering approach for each surface type. It is enabled by default for the Artec Spider scanner.
For some examples of the various model-rendering modes, see Figure 71.
To choose a shading method for the solid fill, use the View menu:
- Smooth shading
- the color value for each point in a triangular face is calculated using color interpolation at the vertices
- Flat shading
- all the points on a triangular face are assigned the same color
Lighting, Color and Texture¶
The Lighting option in the View menu or in the toolbar, or L hot key toggles the lighting in the 3D View window. This option may be useful when you must turn the lighting off to see only the outline of the model or to assess texture quality.
The Color subgroup in the View menu or Color mode section in the toolbar list the methods for assigning colors to the surfaces in the 3D View window:
| Texture | displays textured data; otherwise, the software uses the scan’s default color |  |
Ctrl+Alt+1 |
| Scan color | displays the default color of the scan; the figure depicts two scans |  |
Ctrl+Alt+2 |
| Surface color | displays each frame in a scan using a different color |  |
Ctrl+Alt+3 |
| Max error | colors the frames from Eva and Spider in accordance with their registration quality from green to red via yellow and orange; red indicates unacceptable values and registration errors |  |
Ctrl+Alt+4 |
| X-ray | beneficial for noisy data since it highlights only areas with high point density; it features a slider for adjusting its intensity |  |
Ctrl+Alt+5 |
Back-Face Rendering¶
Artec Studio offers three methods for rendering a frame’s back face:
- Show
- assigns the back face the same color as the model
- Cull
- the back face is not displayed
- Black
- renders the back face in black
You can choose the mode from the View menu or from the toolbar in 3D View window. See Figure 73 for examples that illustrate the different methods of back-face rendering. Black is the default mode.
Representation of Normals and Boundaries¶
The Show normals option in the View menu enables or disables rendering of normals for each vertex. By default, the normals point away from the model surface and toward the 3D scanner. You can change this direction using the Invert normals command. You can also switch between modes for displaying normals by hitting the N key with the 3D View window active.
When working with edges, the Show boundary feature in the View menu allows you to enable and disable highlighting of the model’s edges. To toggle this feature, hit the B key with the 3D View window active.
Rendering and Texturing Untextured Polygons¶
Textured models may have some untextured areas (for instance, the green area in the middle of Table 8). The Render polygons without texture option in the View menu allows you to toggle rendering of such areas.
If the texture of the imported model is smaller than the model itself, Artec Studio can wrap it to fill the untextured areas (see Table 8). The wrapping effect is similar to floor tiling or a repeating wallpaper pattern—that is, the texture repeats periodically. To activate this option, enable the Wrap texture coordinates option in the View menu.
| Options Enabled | Result |
|---|---|
| None |  |
| Render polygons without texture |  |
| Wrap texture coordinates |  |
Displaying Boundaries of Texture Atlas¶
Textures applied to 3D models are obviously two-dimensional. You may, however, want to see the boundaries of each texture patch on the actual 3D surface. Artec Studio can display a texture-atlas file, such as the the middle image in Figure 118, with its boundaries highlighted (see Figure 74). Identifying the way in which the boundaries lie on the surface may, for example, help you determine whether you must simplify the model to get better texture application.
To enable boundary display, access the View menu and select Show texture boundaries or hit the Shift+B keys with the 3D View window active. To disable this feature, make sure this menu command is unchecked.
Technically, this command also works for textures produced by triangle methods, but it provides no usable information.
Saving Screenshots¶
You can capture surfaces displayed in the 3D View window and save them in a graphics file. Unlike the conventional system Print Screen command, this option saves only the contents of the 3D View window and uses the specified background color (see Background for screenshots transparent, black or white).
Tip
When saving screenshots in X-ray mode, avoid using transparent background.
To capture a screenshot, follow this procedure:
- Select the Save screenshot… option in the View menu, or hit Shift+Ctrl+S.
- In the dialog, specify the destination folder and file name, then click the Save button. Artec Studio will save the file in
PNGformat.
Note
If you save a screenshot using an existing file name, Artec Studio will overwrite that file without warning. Be sure to specify a unique file name to avoid overwriting other files.
 ) near the navigation cube (see
) near the navigation cube (see 





