Scanning¶
Scanner Buttons and Capture Modes¶
Your 3D scanner may be in one of the following capture modes (each of which has a corresponding color and flicker rate of the LED indicator on the device):
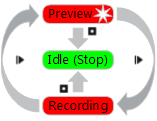
Figure 64 Understanding capture modes (colors correspond to scanner LED indicator colors).¶
- Idle—the LED is steady green
 .
. This mode indicates either that the application has detected the scanner or that the user has clicked the Stop button in the Scan panel or pressed the
 button on the scanner body (see Figure 40). In this case, the 3D scanner is not flashing.
button on the scanner body (see Figure 40). In this case, the 3D scanner is not flashing.- Preview—the LED is flashing red
 .
. In this mode, the 3D scanner is capturing images, but the software is neither performing alignment nor recording captured frames. To start this process, either click the Preview button in the Scan panel (see Figure 84), press the
 button on the scanner body or hit the F7 key on the keyboard. This mode is useful when doing the following:
button on the scanner body or hit the F7 key on the keyboard. This mode is useful when doing the following:Checking the 3D scanner’s field of view
Determining the best position for the object
Preparing to recording and developing a scan procedure
Adjusting texture brightness
- Recording—the LED is steady red

Scanning takes place in this mode, with the software storing 3D data to disk or RAM. Activate this mode either by clicking the Record button in the Scan panel, hitting the Space key on the keyboard or pressing the
 button (do so once for Preview and a second time for Recording). To pause recording, either click Pause in the Scan panel, press
button (do so once for Preview and a second time for Recording). To pause recording, either click Pause in the Scan panel, press  on the scanner body or hit the Space key.
on the scanner body or hit the Space key.
Selecting and Preparing Objects for Scanning¶
Artec 3D scanners employ the structured-light method of 3D reconstruction. Since they capture 3D frames using optical technology, some types of objects are difficult to scan. Certain techniques, however, enable successful scanning of such objects. For example, you can cover a transparent or dark object with a light paint or dust it with talcum powder. You can also use other easily removable substances or a special anti-glare spray.
Surface Features |
Possible Solutions |
|---|---|
Black or very dark |
Dust with anti-glare spray |
Shiny or reflective objects |
Dust with anti-glare spray, tilt scanner when capturing |
Transparent (glass, certain kinds of plastic, etc.) |
Dust with anti-glare spray |
Thin edges |
Add background geometry (e.g., crumpled paper) |
Note
If your scanner supports the HD mode, then you can capture dark or shiny surfaces in high resolution, in their original shape and with no extra steps. See HD Scanning and HD Reconstruction for details.
Technique¶
Artec 3D scanners capture objects at a rate of 15 frames per second to ensure that adjacent frame areas overlap as you gradually move the scanner. Artec Studio uses features in overlapping areas to automatically align captured frames. It performs this task in real time, providing immediate access to the frames in a single coordinate system. You can evaluate the captured area after the scanning session to determine which parts of the object require additional scanning.
Figure 65 Scanner orientation and reconstructed surfaces.¶
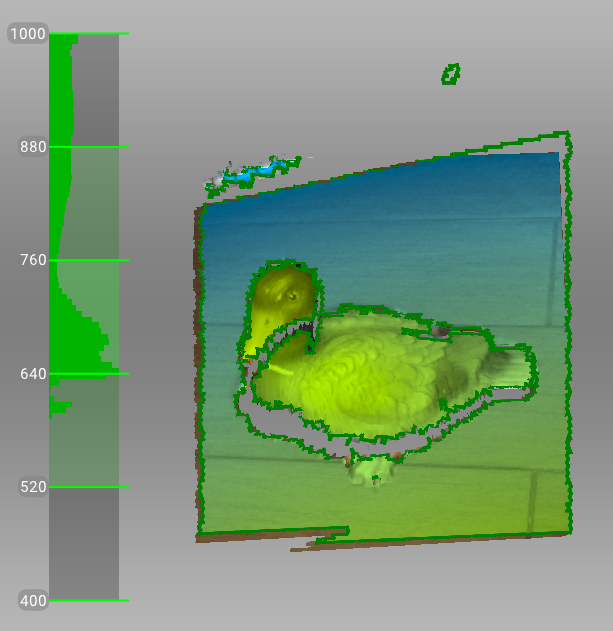
Figure 66 Distance meter and distance color showing surfaces that fall within the optimal range for Artec Eva.¶
To accurately capture an object or scene, follow these steps:
Pay closer attention to the object on the screen rather than looking at the actual object.
Ensure that Artec Studio can accurately register frames from the scanner. To this end, do the following:
Don’t move the scanner too fast
Keep the object as close to the center of the field of view as possible
Maintain the scanner orientation in such a way that the field of view is sufficiently filled with surfaces (see Figure 65)
Try to position the scanner in the way the most surfaces in the field of view are colored in green which corresponds to the center of the range meter 1 (Figure 66)
If you’re capturing an object over several scans, remember to capture a common area in each one to ensure successful alignment
If you’re capturing an object in one scan, do so all the way around the object—regardless of direction—plus a little more (360+ degrees)
Avoid capturing any objects that may change shape during the scanning process. When the geometry of the scene is changing, the system may fail to find the correct position of new frames relative to previously aligned ones. If you have captured unwanted objects, you must remove them later during the editing stage (see Editing Scans).
Don’t record too many frames: ensure that you have sufficiently scanned all regions, but avoid scanning them twice, except when providing overlapping areas for subsequent alignment.
- 1
Technically, the center of the range meter is the center of the depth of view. The 3D scanner has near and far cutting planes (see Figure 39) that determine the optimum distance between the scanner and the target object. Artec Studio offers the Range meter feature so you can easily visualize the distance between the scanner and the object during the recording process. The Range meter comprises a set of semitransparent diagrams located on the left side of the 3D View window (see Figure 66). Each histogram displays the distribution of captured surface points by distance from the scanner. The color corresponds to the set of surfaces from which it was obtained: by default, gray indicates registered key frames, dark green indicates the last successfully registered frame and red indicates a registration error.
Scanning Procedure¶
Prepare the object and make sure it has enough geometry and texture details (see Selecting and Preparing Objects for Scanning).
Provide even lighting without using direct sunlight.
If you have connected just one 3D scanner to the computer, Artec Studio will select it automatically; otherwise, you must select the appropriate device from the dropdown list under the Advanced section of the Scan panel.
If your selected 3D scanner supports the HD mode (such as Artec Eva) and you want to get the scanned images in high-definition resolution, you need to turn the HD mode on (see Enabling HD Mode for details).
Create a new project before getting started: select from the menu, or use the shortcut Ctrl+N.
Decide how many sessions you need in order to capture the entire object. By using the Artec turntable, you may be able to avoid interrupting the session and eliminate the need to turn the object by hand. Depending on your choice, you may
Turn the object
Position yourself to gain access to the other area
Use a rotating table
Click Preview or press
 on the scanner. Direct the scanner at the object and practice your movements around the object, taking into account the proper Technique.
on the scanner. Direct the scanner at the object and practice your movements around the object, taking into account the proper Technique.Note
If you have checked the Enable automatic base removal option (it is disabled by default), then first direct the scanner at the surface that supports the object.
Click Record to start capturing.
Gradually move the scanner while monitoring the process in the 3D View window
Capture what you can and pause or cease recording by clicking the Pause or Stop button, respectively. Choose Stop if you must make adjustments to the object’s positioning (see the next step).
Turn the object or otherwise adjust it as necessary, then capture any remaining unscanned regions.
Once you have successfully captured the object from all sides, click the Stop button or press
 on the scanner body.
on the scanner body.
HD Scanning and HD Reconstruction¶
While all Artec scanners can scan 3D objects in the standard-definition (SD) resolution, Artec Eva and Artec Leo also support an HD mode — AI-powered scanning technology for ultra-sharp, clean, and detail-rich scans.
Key advantages of the HD mode:
Scanning with a high resolution of up to 0.2 mm
Broad range of objects that can be scanned flawlessly and in high detail: from smaller, intricate parts like valve handles, to larger areas with fine details like car engines
Little to no noise in raw data for cleaner post-processed data and saved time for your final 3D model
Capability to capture dark or shiny surfaces in high resolution, in their original shape and with no extra steps
To obtain HD scans from the data captured in the HD mode, Artec Studio provides you a special algorithm of HD data processing — HD reconstruction. This algorithm generates large, high definition frames with more details to give you complete surface geometry.
In general, the HD reconstruction is a time-consuming and resource-intensive operation. It requires:
Powerful Nvidia video card
Sufficiently large RAM
However, you can optimize the HD reconstruction by properly choosing its main parameters:
Point density, which determines the number of points per frame used for data processing
HD frames frequency, which determines the fraction of captured HD frames to be used for the HD reconstruction
See Enabling HD Mode for details.
Important
To obtain HD scans with your 3D scanners, the HD mode should be enabled in advance, before scanning or importing the HD data.
To find out more on the HD scanning and HD reconstruction with Artec Eva, see Notes on HD Scanning With Eva.
Setting the HD mode for Artec Leo is described in the Artec Leo manual. For information on importing the HD data from Artec Leo, see Opening a Project from Leo.
Tracking Modes¶
The software provides three tracking modes and one option:
- Geometry + Texture, or hybrid
The optimal (and default) algorithm for 3D scanners equipped with a texture camera. It uses features from images obtained using the texture camera as well as geometrical features of the object and thus is more likely to successfully capture flat or textureless objects. The only possible drawback is greater CPU utilization compared with other algorithms, potentially decreasing the frame rate for less powerful computers. You can use this mode with Artec MHT, Artec Eva, Artec Spider, and Artec Spider II.
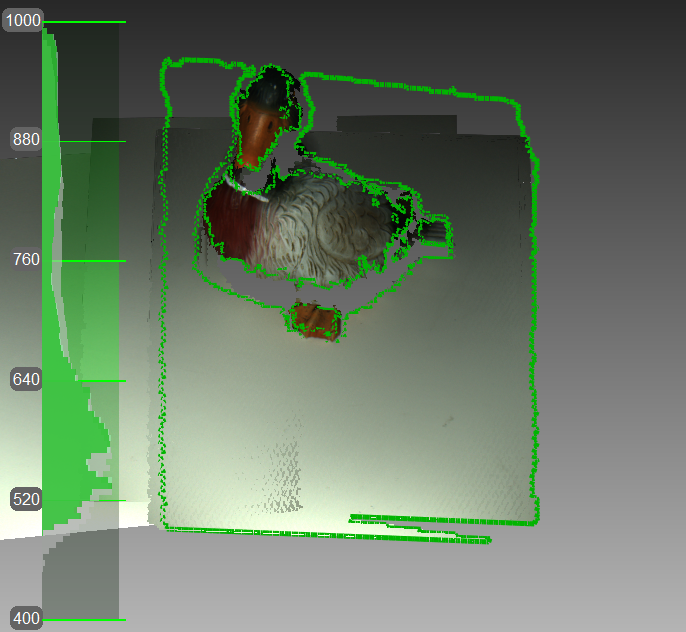
Figure 67 Texture tracking renders color object (scanner’s current field of view outlined in green).¶
- Geometry
The default algorithm for all 3D scanners that lack a texture camera (Artec Eva Lite). It uses only object geometry to align the scanned frames, making it suitable for objects that have a rich geometry but not objects with large flat, spherical or cylindrical parts. The Geometry tracking algorithm is the least CPU hungry.
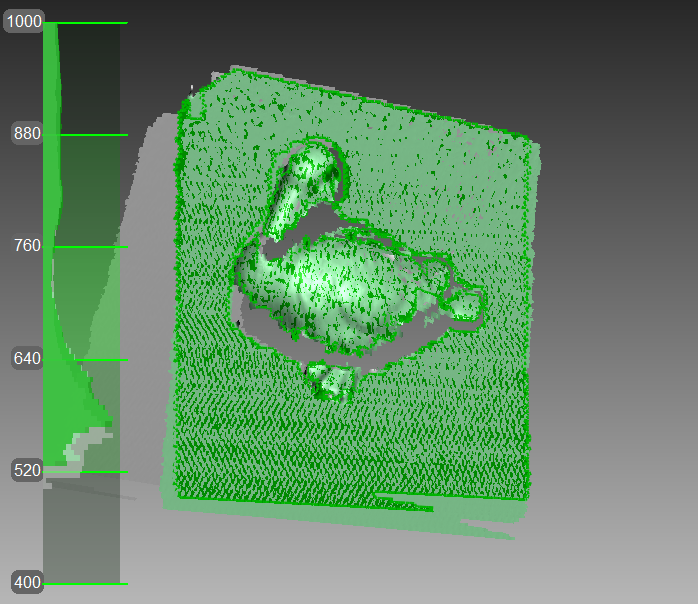
Figure 68 Main window when using Geometry tracking to scan objects.¶
- Targets
A special algorithm for scanning objects with special targets placed on their surfaces. See Target-Assisted Scanning.
- Real-time fusion (option)
Available for Artec 3D scanners, this option fuses the results immediately after scanning.
See also
Base Removal: Erasing a Supporting Surface¶
When you capture an object, you can often omit from the scan any surface that supports the object. The Base removal option serves this purpose. To employ this option, first indicate the surface on which the object is resting and then capture the object. If this approach is unsuitable for your situation, clear the Enable automatic base removal checkbox.
Open the Scan panel.
Check the Enable automatic base removal option (it is disabled by default).
Click Preview and direct your scanner at the surface that supports object (e.g., a table or the floor). A gray wireframe plane will appear, indicating the scene’s base.
Once the application detects the base, it will display a message: “Now scan the object.”
Important
If Artec Studio fails to detect a supporting surface, you can still start recording.
Click Record (
 ) and then direct the scanner at the object.
) and then direct the scanner at the object.Scan the object freely. You can pause and resume the session as necessary.
Click Stop; all scans will move to the coordinate system with the Z axis normal to the base.
Close the Scan panel. The Base removal algorithm will remove the previously detected supporting surface. If not, erase it manually.
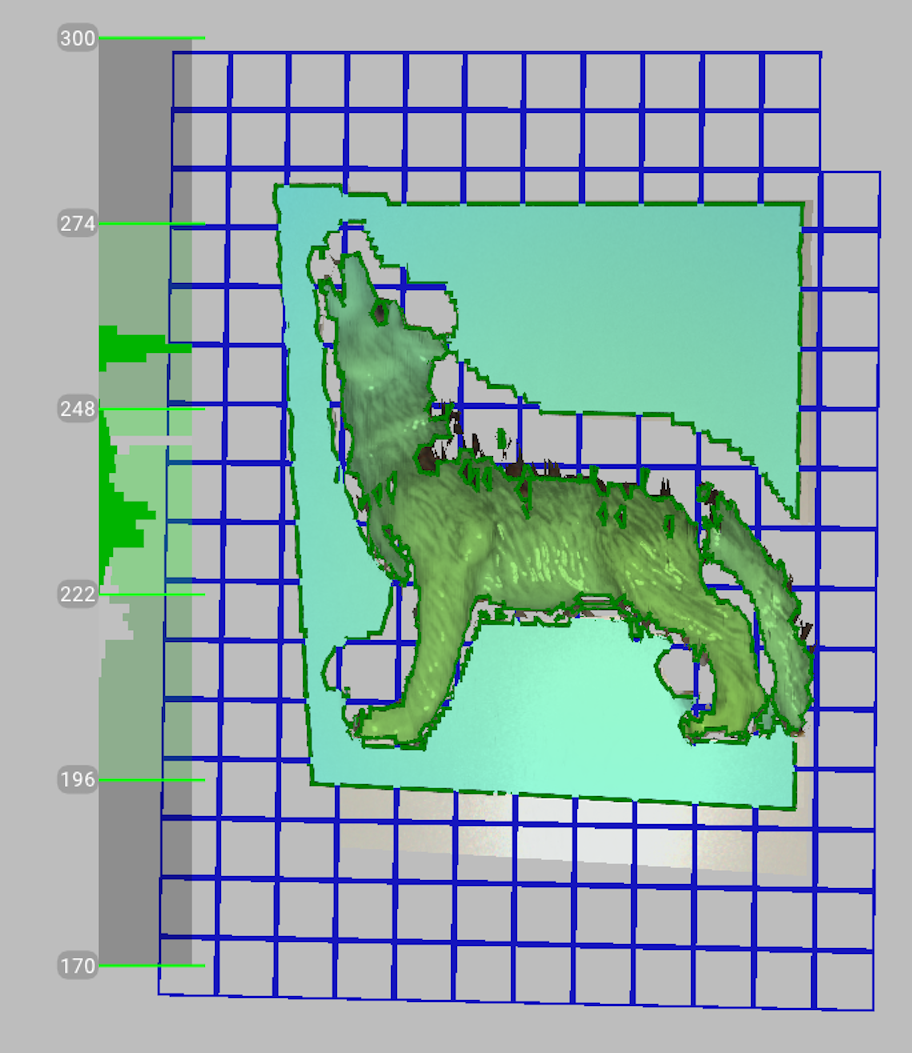
Figure 69 Scanning with the Enable automatic base removal option.¶
Resuming Scan After Lost Tracking¶
Artec Studio records adjacent frames on the basis of common surface features. If the scanner stops recognizing common features, it will stop capturing the scene. This situation is called lost tracking; if it happens, just direct the scanner at a recently captured region. There are, however, nuances, which we address below.
Table 2 lists several causes of lost tracking. The most common is moving the scanner too fast.
Reason |
Possible Solutions |
|---|---|
Moving the scanner too fast |
Move the scanner more slowly or increase the Scanning speed |
Scanner sees too few surfaces |
Apply an anti-glare spray or direct the scanner at a larger part of the object; increase Sensitivity of Artec Spider |
Object doesn’t have enough features for successful tracking |
Apply masking tape or draw markers on the surrounding surfaces, and/or move the scanner more slowly |
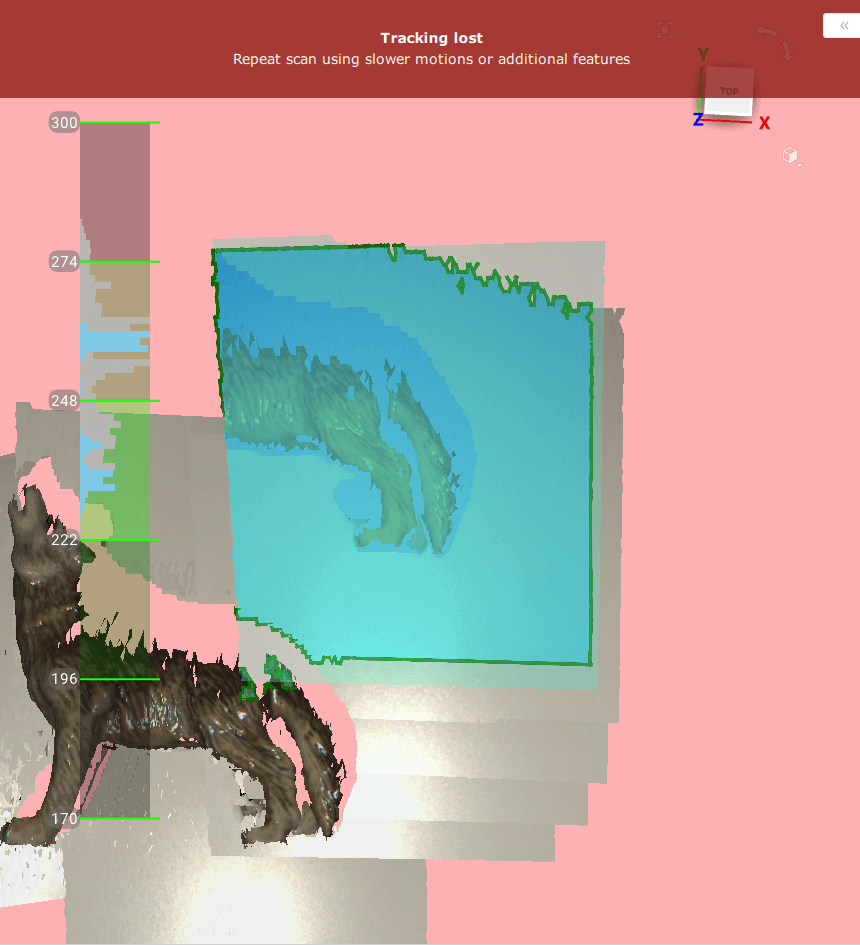
Figure 70 Alert message: tracking lost.¶
The Scan using auto-alignment option may ease the process of resuming tracking (this option is enabled by default in the application settings). Note the following:
Artec Studio switches almost instantly from displaying Tracking lost mode (see Figure 70) to Searching for position, which appears on a green background.
To continue scanning, direct the scanner at a region you’ve already captured.
Try to maintain the original scanner orientation toward this region
You need not necessarily use the most recent one, but it should have sufficient texture features.
If the application successfully resumes tracking, it will start recording in a newly created scan. This new scan will already be aligned with the previous one. All the scans will also be grouped.
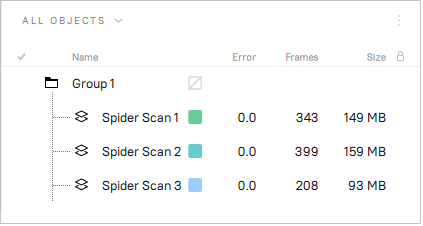
Figure 71 Workspace panel after resuming tracking.¶
The Scan Using Auto-Alignment section describes system behavior when this option is disabled.
Auto-align new scans with those marked in Workspace¶
Auto-alignment is a great timesaver and may help simplify further processing. But for projects that involve scans using Geometry + Texture tracking and for which the actual scene is unchanged, you can continue scanning immediately:
Ensure that the Scan using auto-alignment option is turned on in Settings (see Capture).
Mark previously captured scans using the
 icon in the Workspace panel.
icon in the Workspace panel.Select Geometry + Texture tracking as well as the Auto-align new scans with those marked in Workspace checkbox in the Scan panel.
Click Preview, direct the scanner at a textured region you’ve already captured textured region—maintaining the original scanner orientation—and then click Record.
If tracking resumes successfully, Artec Studio will align the newly recorded scan with the selected ones.
Scanning With Real-Time Fusion¶
Real-time fusion is a special mode in which Artec Studio builds a 3D model in real time while you’re scanning. It’s the easiest and fastest way to obtain a model, but it cannot completely replace the normal workflow for processing raw scans after capturing them. Thus, we recommend avoiding Real-time fusion in the following cases:
The scene is large and the amount of GPU memory is limited
Objects have complicated shapes that cannot be captured in one scan session
The object has small geometric details
Extra-high accuracy is required
Figure 72 Real-time fusion model.¶
The Real-time fusion feature is available for each tracking method.
Open the Scan panel.
Select the required tracking mode.
Select the Real-time fusion checkbox 2.
Click Preview and then Record. Observe the recommendations in Scanning Procedure.
Pause and resume the session as necessary.
When you stop scanning, the Workspace panel will add one or more raw scans named
Spider Scan1,Spider Scan2,Spider Scan3and so on, as well as one model namedSpider Scan1-Fusion. The number of these raw scans corresponds to how many times you pause and resume scanning (see Figure 73).
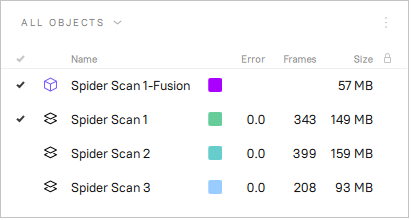
Figure 73 Workspace panel after using Real-time fusion.¶
You can access the Settings window and use the Performance tab to configure the following Real-time fusion settings (see Real-Time Fusion Settings):
- Voxel size
3D resolution of the model (i.e., the size of the triangulation-grid step in millimeters). The smaller the value, the more geometric details you can detect and capture in 3D.
- 2
If you selected the Targets mode and cleared the Disable hybrid tracking for .obc checkbox (see the Photogrammetry Settings section), Artec Studio will clear the Real-time fusion checkbox because it doesn’t support this combination of options.
AI Photogrammetry¶
Starting from Artec Studio 19, two new algorithms have been added to allow users to reconstruct 3D models from sets of photos and videos without a 3D scanner and a photogrammetry kit. Please be aware that projects created by this version might not be compatible with older versions of Artec Studio.
The Photo Reconstruction pipeline in Artec Studio is divided into two consecutive stages:
Create Preview: positions photosets in 3D space, generating a photo scan as the output.
Create Model: creates a final 3D mesh that can be further processed and textured.
Both these algorithms are available in two types:
Separate Object is intended for a single object that is fully captured within the frame and clearly separated from the background.
Whole Scene is suitable for feature-rich scenes, such as aerial or drone captures, or objects like stones, statues, and architectural structures, where there is no requirement to separate the object from the background.
See also
For more details on the full workflow of AI Photogrammetry, preparing objects for the algorithms, their basic and advanced settings and hardware limitations, please refer to the Quick Start Guide and the Full User Manual .
Target-Assisted Scanning¶
Generally, you don’t need any special equipment to record using an Artec scanner. If the object has hard-to-scan regions, however, targets may be useful. In some cases, they can improve tracking and further registration.
Targets address the problem of increased deviation when scanning large objects and provide more scanning accuracy by very precise ongoing alignment. Starting from version 17, Artec Studio gives you the ability to evaluate the quality of reference targets capturing when scanning. You can view the distribution of error deviation across the whole set of the reference targets (see Inspecting Quality Of Targets Clouds Registration).
Placing Targets¶
Whatever the method chosen, you should place at least non-coded targets on the object.
Attach non-coded targets (Figure 74) to the object using the following rules:
Try to place them on flat elements
Avoid uneven surfaces
Avoid obstructing significant geometric elements

Figure 74 Non-coded targets placed on an object.¶
Note
You can specify the target size in the Settings dialog of Artec Studio, as Photogrammetry Settings describes. If you use non-coded targets from the Scan Reference kit, specify 5 mm for the inner diameter and 10 mm for the outer diameter. You should measure targets from other suppliers and specify both diameters in the appropriate fields of the Settings dialog.
Place coded targets if your choice is photogrammetry (Photogrammetry Solution).
Prepare the objects and surrounding scene. All objects must remain stationary during measurement and capture.
Place the cross (Figure 76) on the scene, ensuring that it rests firmly, and it is seen from most points of view. Also double check that all targets on the cross are clearly visible.
Place the coded targets on the object and the surroundings. Note that you should distribute them such that at least six to eight coded targets are visible in each image. Random placement is preferable; avoid symmetry and target alignment.
Figure 75 Coded targets.¶
Using Artec Scanners Only¶
You don’t necessarily need a photogrammetry kit to benefit from targets placed on the object you’re scanning; Artec 3D scanners can do all the work. This mode employs extra-hybrid (Geometry + Texture + Targets) tracking and doesn’t require you to upload an OBC file.
Open the Scan panel in Artec Studio. Select Targets under Features to track.
Scan the object from all sides
Note
As you scan (without having uploaded an OBC file), the application registers the target coordinates. You can then save an OBC file and use it in later scanning sessions. We strongly recommend running Global registration first, however.
Photogrammetry Solution¶
By using a combination of special reference targets and photogrammetric measurements, you can scan large areas in one session, improve the accuracy of captured surfaces and boost productivity by reducing postprocessing time. The only downside of this method is the preparation. After scanning, however, you need not align the scanned surfaces, so you can immediately proceed to Fusion (see the order of postprocessing steps in 3D Scanning at a Glance).
This synergy of technologies is possible thanks to Artec 3D-scanner and photogrammetry solutions. Several third-party photogrammetry offerings are available on the market. Scan Reference photogrammetry is one example. The Scan Reference kit includes hardware and software (see Figure 76), a digital camera, a reference-scale cross, non-coded sticky targets (which Artec Studio uses to match the captured 3D data to the photogrammetric measurements), and reusable magnetic coded targets (required to automatically carry out measurements in the Scan Reference software).
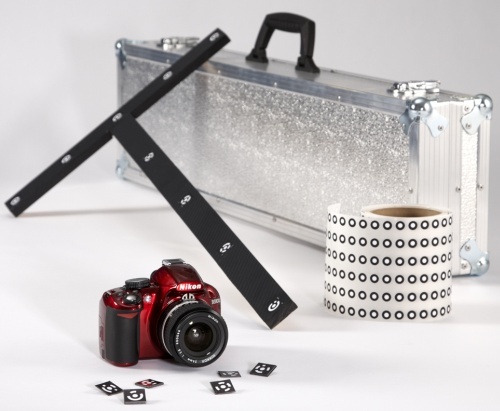

Figure 76 Scan Reference kit¶
The kit includes (from left to right) coded targets (foreground), a digital camera, a scale cross, a roll of tape with non-coded targets and a carry case.
Preparing To Scan With Targets¶
Take several photos of the object from different angles. To determine the appropriate number of photos, angles and targets for each image, as well as required settings for a calibrated digital camera, consult the Scan Reference user manual and FAQ article. General recommendations are as follows:
Take photographs at a distance of 0.5–1.5 meters with enabled flash
Each photograph should contain as much targets as possible and each target should be captured at least in 10 photos
Entire cross should be captured in first 10–12 photographs
Capture the object from all sides
Move the cross and the coded targets away from the scene.
Connect the camera to a PC, then transfer and process the photos using the Scan Reference software. Once the calculations are complete, the software will display measurement results on the screen. These results can appear as a point table or a 3D model.
Save the table of points in an
*OBCfile. This format is the software’s default.
Scanning Procedure With Targets Clouds¶
To perform scanning using targets, follow these steps:
Import one or more target clouds (
OBCfiles), using the File → Import → Scans, meshes or point clouds menu option or press Ctrl+I. You can also drag and drop the files to the area of the 3D View window. The imported objects will appear in the Workspace panel and will be rendered in the 3D View window.Open the Scan panel in Artec Studio. Select Targets under Features to track.
Select a targets cloud to use as a reference from the dropdown list below.
Important
If you don’t want the texture and geometry features to assist target scanning, select the Disable hybrid tracking for .obc checkbox (Photogrammetry Settings).
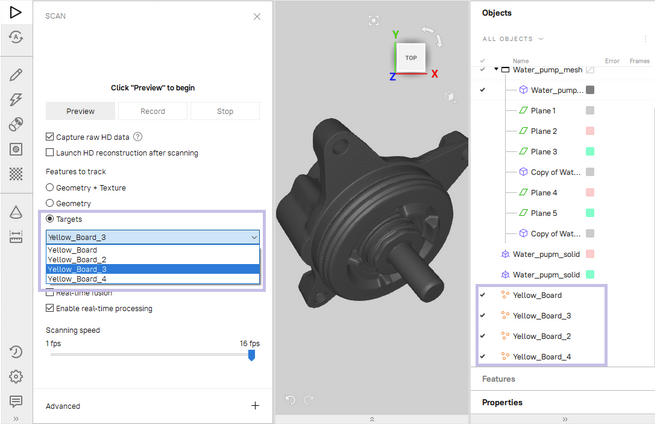
Figure 77 Example of targets clouds uploaded.¶
Scan the object. When you finish, the software will automatically align and register all scans.
Check the quality of targets’ registration (see Inspecting Quality Of Targets Clouds Registration).
If you have introduced changes to the captured targets cloud on step 5, run Global registration.
If necessary, repeat steps 5 and 6.
Inspecting Quality Of Targets Clouds Registration¶
To increase the accuracy of scanning with targets and give users more control and flexibility, an ability to manually inspect the quality of target clouds registration is implemented in Artec Studio.
During scanning, each reference target is captured in a number of frames. The result of target capturing in a particular frame is called an instance. All instances representing the same target are grouped into a cluster. During global registration, Artec Studio calculates the deviations of each captured instance and cluster from the corresponding targets of the reference target cloud.
The deviation values are listed in the Features Panel. They are also shown in the 3D View window. For every instance, its position, its center and deviation can be viewed. The size and the color of the target represents how much it deviates from the reference position.
You can evaluate the deviation of each instance or cluster and exclude badly registered targets from the consideration of the global registration algorithm.
Features Panel¶
By default, the Features panel is available above the Properties panel at the bottom of the Workspace panel. It contains the list of clusters and instances of all targets captured during scanning, including deviations from their reference positions.
For the Features panel to display the list of captured targets, you need to select proper objects in the Workspace panel. These can be one or more scans with the global registration applied and/or the reference target cloud.
Tip
To work easier with the Features panel, drag it to the area of the 3D View window.
Evaluating Deviations¶
For each cluster and each instance inside the cluster, Artec Studio calculates its deviation. The value of the deviation depends on the type of objects selected in the Workspace panel:
With one or more scans and the reference targets cloud selected, the deviation is calculated against the position of the corresponding reference target.
With only scans selected, the deviation is calculated against the average position of the captured instances of the reference target.
With only the reference targets cloud selected, no deviation is provided.
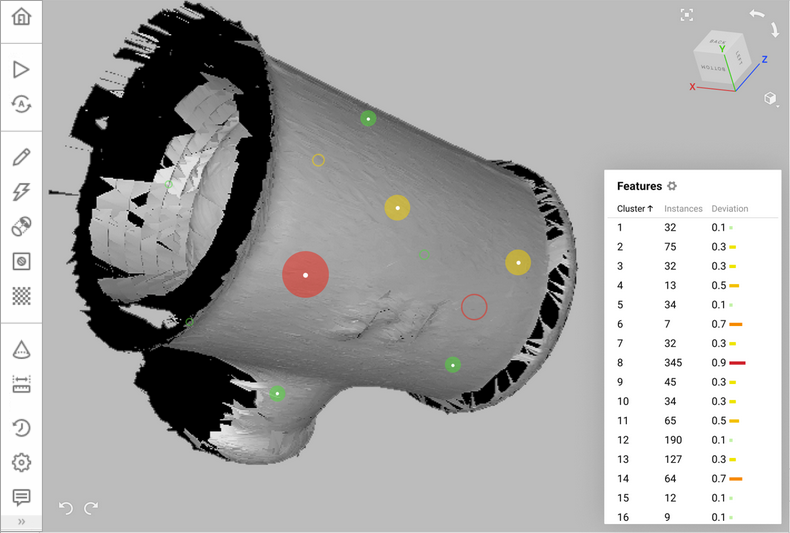
Figure 78 The list of instances belonging to a cluster and their deviations are displayed in the Features panel and in the 3D View window.¶
You can inspect the deviation of the entire cluster or analyze any of its instances separately. To view the list of instances inside a cluster, click the ![]() icon to the right of the number of instances. To return to the list of clusters, click All clusters.
icon to the right of the number of instances. To return to the list of clusters, click All clusters.
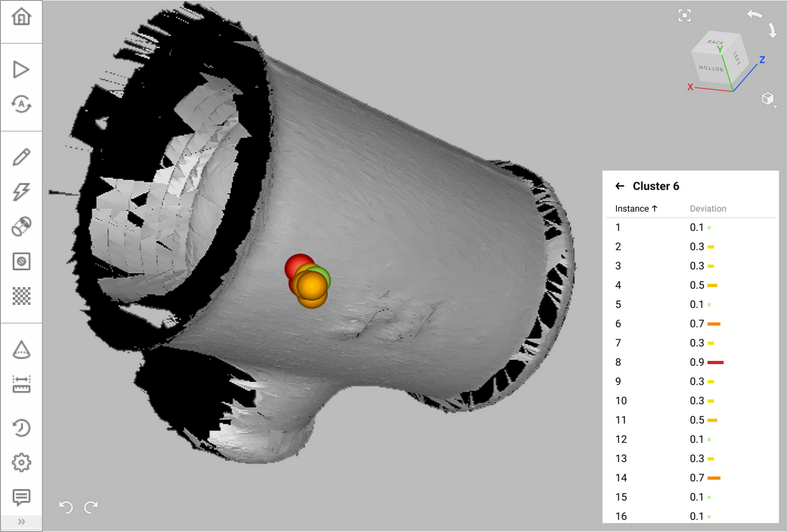
Figure 79 The list of clusters and their deviation displayed in the Features panel and in the 3D View window.¶
Removing Badly Registered Instances/Clusters¶
To remove a badly registered target instances or clusters from further registration process, follow these steps:
In the Features panel, select one or more instances or clusters of the desired scans.
Open the context menu by clicking RMB on the selected object(s) and click Delete. You can also press Delete on the keyboard.
After you have excluded the selected targets, re-run Global registration.
Note
You can also measure distances between individual instances in the targets cloud. See Measurement Tools.
Artec Metrology Kit¶
Artec 3D introduces the new Artec Metrology Kit available for Artec Studio versions 17 and above. The kit is basically a camera-based photogrammetry system that enables you to both generate a reference target clouds (.obc) and evaluate results directly in Artec Studio, with an integrated software. Using the kit, you can measure objects of any size, and the resulting target cloud can be used for applications like deformation analysis, flatness inspection, general dimensions measurement, or your own specific engineering use case.
The kit has been developed to complement the photogrammetry-based Artec product line. It can be used in conjunction with our scanners to attain maximum accuracy and error-reduction.
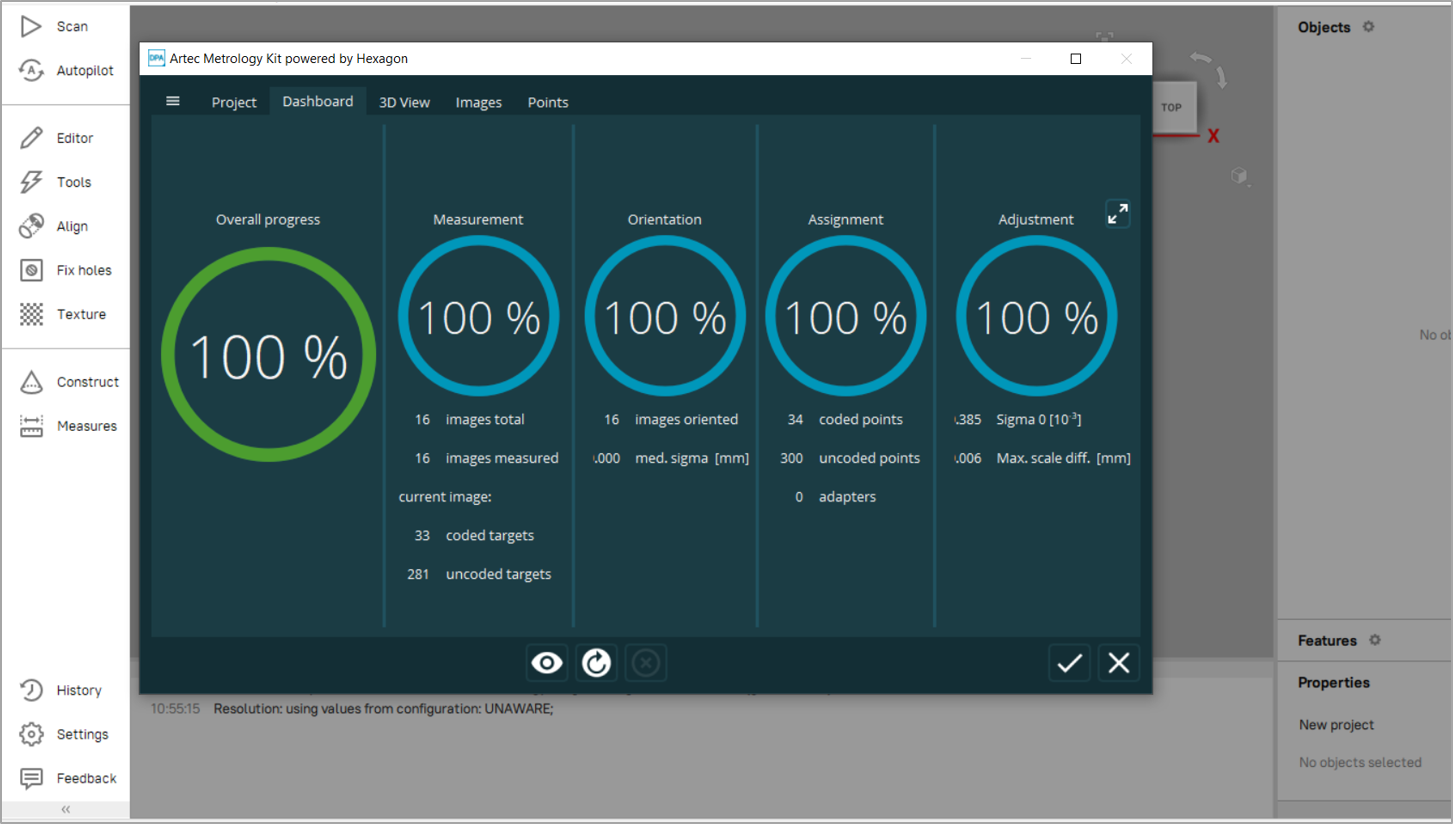
Figure 80 The Artec Metrology Kit software integrated into Artec Studio.¶
There are two types of kits available:
The Artec Metrology Kit Entry and
The Artec Metrology Kit Professional
The difference between the two is only the hardware that comes with the kit - the camera and reference objects.
Each kit contains the following hardware:
Camera and camera Flash
Reference crosses and scale bars
Coded and non-coded targets
Batteries and SD card reader
Important
The Artec Metrology Kit software is integrated into Artec Studio, immediately after the kit is activated.
The Artec Metrology Kit can be used independently or along with other Artec scanners.
Activating the kit¶
The first step requires you to activate your Artec Metrology Kit using the Artec Installation Center. Activating the kit automatically enables the Artec Metrology Kit software in your system.
Capturing photos¶
Prepare the object to be captured by placing the reference crosses, scale bars and targets on surfaces, ensuring that they don’t move relative to the object.
The scale bars must be places perpendicular to each other.
Make sure there are non-coded and coded targets in each photo. Capture each target at least 6 times, and the reference cross from four perpendicular angles.
Follow the best practices of photogrammetry (See section on placing targets above).
Creating reference cloud¶
After capturing all the photos, to generate a reference target cloud, follow these steps:
Make sure you have activated your Artec Metrology Kit in the Artec Installation Center. Doing so, automatically activates the Artec Metrology Kit software in Artec Studio.
In Artec Studio, go to Files → Generate reference cloud… option. This will launch the Artec Metrology Kit software.
Enter an appropriate project name and select the respective project template from the drop-down list. Every kit has a unique template.
Click on the Next button, and on the next window, the DPA pilot measurement dialog box opens up.
Select and upload all the captured photos (from the file system or an SD card), and click on the OK button (tick mark).
Set a target thickness value in open dialog. This value will be automatically subtracted from the surface for precise result. You can find the set value in the Properties panel of the Workspace (See Figure 82).
Wait for the software to perform the calculation and generate a target cloud.
Note
You can use the 3D View, Images and Points options in the menu bar to assess the targets, photos etc. You can also redo the calculation by adding more photos, or changing the settings.
Click on the OK button (tick mark) to generate the reference cloud, which then appears as an object in your Artec Studio workspace.
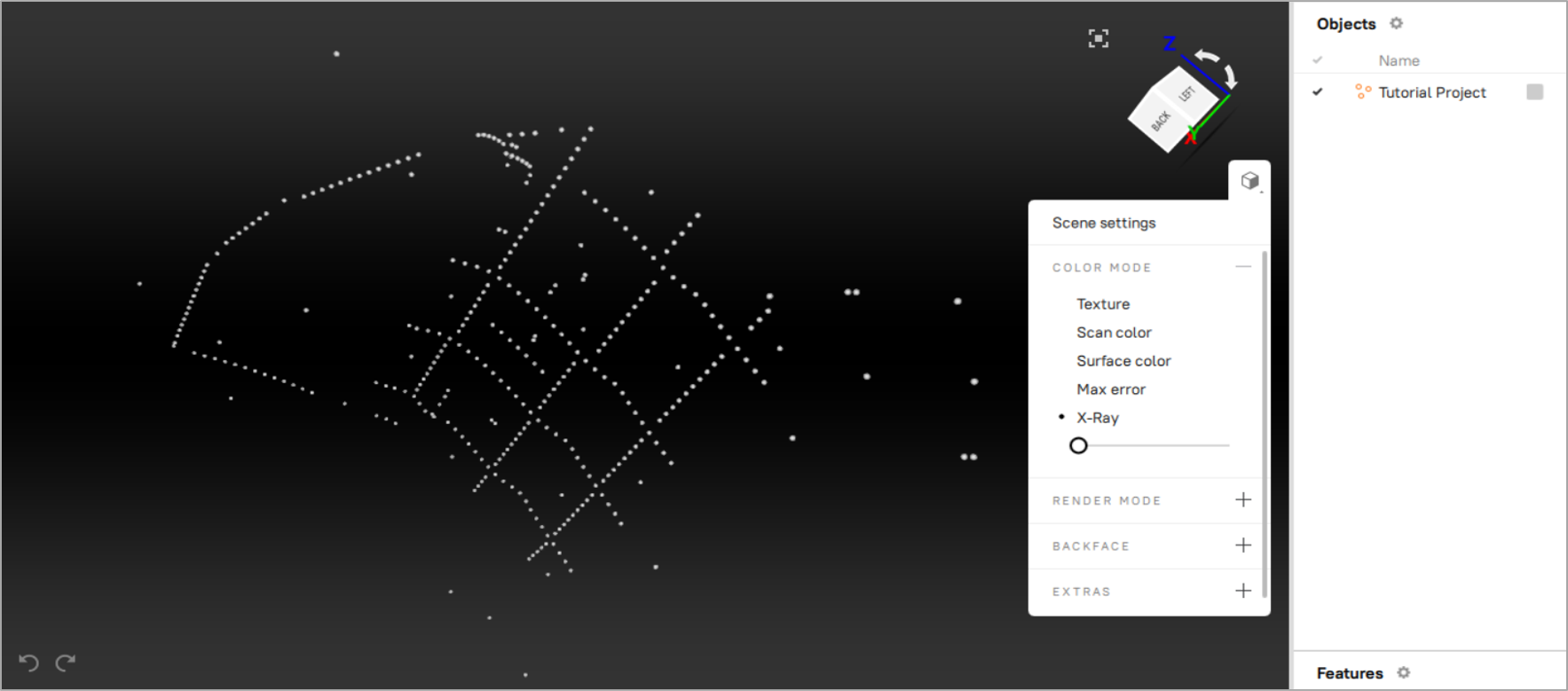
Figure 81 Reference target cloud generated using the Artec Metrology Kit.¶
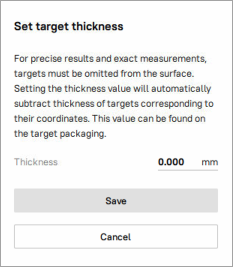
Figure 82 Target thickness compensation dialog.¶
Metrology Kit applications¶
After creating a reference target cloud, you can:
Use the Artec Metrology Kit software to perform inspections or measurements like deformation analysis, flatness inspection etc.
You can also carry on with target-assisted-scanning, or process your scan data in Artec Studio using the generated target cloud. For the detailed workflow, see Target-Assisted Scanning.
Using Certain Scanner Types¶
Notes on Scanning With Artec Point¶
Starting from Artec Studio 18.5, Artec introduces Artec Point, a new automated desktop 3D scanner for digitizing small parts with metrology-grade accuracy. Artec Point uses a blue laser for scanning. The two cameras of the scanner are positioned at specific angles, and their fields of view intersect to form a common field of view. During the scanning process, more than four marker points must be present in this common field of view.
Avoid placing targets on prominent features to prevent the loss of key feature data and ensure there are neither too many nor too few targets.
Double check that objects don’t change their shape and position.
If you feel that the entire object has not been fully scanned, you can scan it again. Each new scanning session will create a new point cloud.
Basic settings
Resolution: Sets the resolution of the output scanned data.
Remove base: Isolates and removes the base that is scanned as part of the object. This feature allows for the base to be identified and deleted while keeping the object intact.
Note
Base removal is only possible when scanning is based on a previously created target cloud and requires at least four targets attached to the base on which the object is placed. If the object is placed on an additional stand that rests on the base as shown in the image below, targets attached to the stand cannot be used for detecting or removing the base.
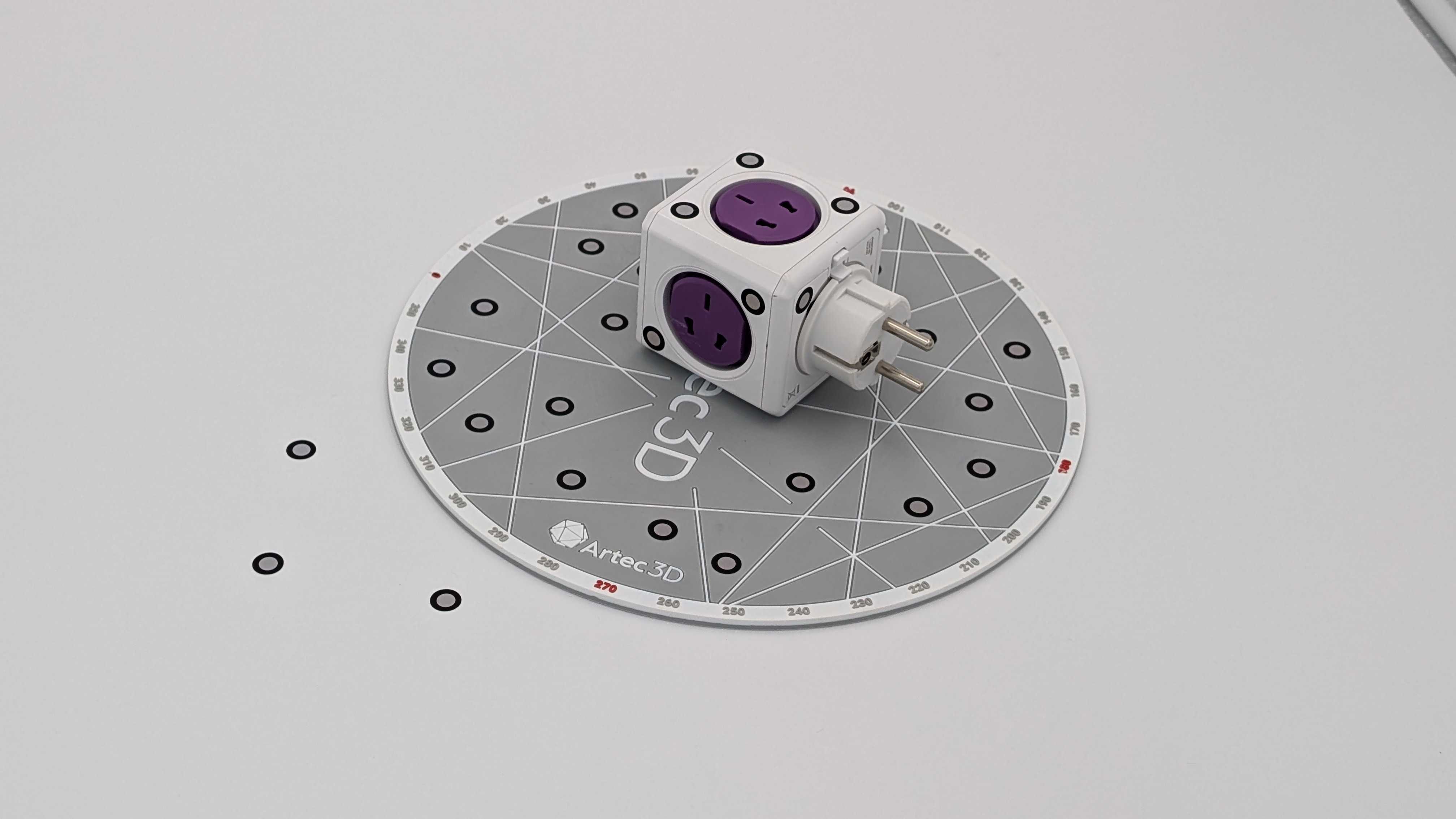
Figure 83 Insufficient amount of targets on the base.¶
Advanced settings
Target size: Determines the size of attached reflective targets:
3 mm
6 mm
12 mm
Target excision: Defines the value for removing points around targets in the point cloud to create smoother edges; the higher the value (0 to 3 mm), the larger the hole but the cleaner the edges.
Base cut-off threshold: Defines the threshold for automatically detecting the base using targets and allows adjustment of the cut-off position upwards from this point, typically within 1–2 mm; the value range varies from 0 to 25 mm.
Laser exposure: Controls the laser illumination time. Decrease it for highly reflective objects. The default value is 1 ms for regular objects, 0.5 ms for larger ones. For capturing finer details, set it lower. The value range is from 0.1 to 10 ms.
Note
When working with data from Artec Point, please follow the standard post-processing workflow as outlined in the user manual. If there are any deviations from the standard workflow specific to Artec Point, these will be clearly indicated in the respective sections of the user manual. Always refer to these sections for any specialized instructions.
Notes on Scanning With Spider/Spider II¶
Because Artec Spider and Artec Spider II have smaller field of view and provides higher accuracy in comparison with Artec Eva, scanning using it can pose difficulties. Consider the recommendations given in Technique and also the following:
Opt for rotating table if possible
Use a piece of paper with text on it as artificial texture
Double check that objects don’t change their shape and position
Try tuning sensitivity in particular cases (see Sensitivity). Avoid extreme values.
For the Artec Spider II scanner, we recommend increasing the Geometry gain slider for better scanning of dark surfaces, as it improves pattern visibility. However, avoid setting it too high to prevent excessive noise on light surfaces. Adjust as needed based on surface color for optimal reconstruction. This setting controls the brightness of the geometry cameras. However, it does not affect the texture camera).
Artec Spider and Artec Spider II scanners work best once they reach their normal operating temperature. As soon as you plug Artec Spider/Artec Spider II in or connect it to a PC, they begin warming up. In the Scan panel, you can see two lines indicating the device’s current and optimal temperatures. Artec Spider/Artec Spider II will warm up faster in Preview mode. The Scan panel also displays additional information about the time remaining until the scanner reaches its optimal temperature.
Note
Artec Spider and Artec Spider II can operate at temperatures beyond its optimal range, but the accuracy of captured surfaces may be lower.
Notes on Scanning With MHT¶
The flash feature in an Artec MHT scanner has a very large but limited number of operation cycles, so ensure that you disable the scanner when it’s not in use. Avoid leaving the Artec MHT on for a long time when using the maximum capture rate (15 frames per second). Artec Studio will automatically turn off the Artec MHT after five minutes of continuous operation. Normally the active mode/rest mode is 3 minutes of scanning and 7 minutes of rest; this mode is optimal and significantly increases the lifetime of the flash.
Notes on HD Scanning With Eva¶
To obtain a scan of high-definition resolution with the Artec Eva scanner, the HD mode must be turned on before scanning. Find out how to do this in Enabling HD Mode.
After the HD mode is enabled, perform your scanning as usual.
Once you finish scanning, the following will happen:
Two new objects will appear in the Workspace panel: a conventional scan of SD resolution and a raw data scan. The latter can be identified by its icon (
 ). Using the obtained raw data scan, you can launch the reconstruction of the HD scan at any time (see Reconstructing HD scans from saved raw HD data for details).
). Using the obtained raw data scan, you can launch the reconstruction of the HD scan at any time (see Reconstructing HD scans from saved raw HD data for details).If the Launch HD reconstruction after scanning option has been selected before scanning, the HD reconstruction will start automatically. The corresponding progress bar will be displayed on the Status bar.
When the HD reconstruction is complete, an HD scan will appear in the Workspace panel in addition to the SD one. Its name will be marked with the letters “HD”, for example: Eva HD Scan 1.
Tweaking Scanning Options¶
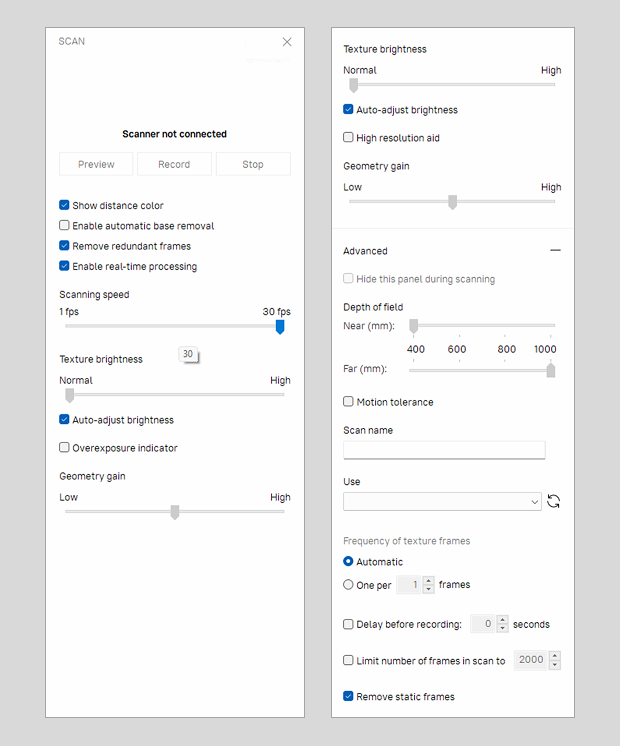
Figure 84 Scan panel: Advanced section hidden (on the left) and revealed (on the right).¶
Enabling HD Mode¶
To perform HD reconstruction, you need to compile the neural network model before using this algorithm. You can do this during your first launch of Artec Studio, or by navigating to the Performance tab in Settings and clicking the Set up neural network button.
If the scanner connected to your computer supports the HD mode (such as Artec Eva), it will be enabled by default. You will see the Launch reconstruction after scanning option selected. The specifics of each of these options are described below.
Launching reconstruction after scanning¶
If the Launch reconstruction after scanning option is selected, HD reconstruction will automatically start as soon as your scanning is complete. Therefore, before you start scanning, you have two options:
To use the common Scan reconstruction slider which adjusts the final quality of reconstructed scans and is the default one.
To use the advanced mode and configure the HD reconstruction parameters: Point density and HD frames frequency manually. To do this, use the eponymous sliders.
The Scan reconstruction slider has four different options:
SD (equivalent to the No HD option for the HD frames frequency and zero Point density respectively)
Normal (equivalent to the 1/8 for the HD frames frequency and Point density of 1.78x)
High (equivalent to the 1/4 for the HD frames frequency and Point density of 4x)
Ultra (equivalent to the 1/2 for the HD frames frequency and Point density of 7.11x)
To adjust the HD frames frequency and Point density parameters, check the Advanced option above the Scan reconstruction slider.
The Point density determines the number of points in the resulting HD scan. The higher the point density, the greater the number of polygons in the resulting HD scan.
The Point density varies in the range from 1× to 16× and is represented by the following values:
Normal
High
Ultra
Extreme
With the value of 1×, the number of points per scan is of the same order as in the case of the SD resolution. However, the surfaces reconstructed from the 1× HD data are cleaner than the ones based on the SD data. The density of 16× corresponds to ~3 million polygons per frame. The default Point density is 4×. This means that the resulting HD scan will contain four times as many points as the SD scan.
Increasing the Point density results in higher degree of resolution, coverage, and detail, but requires more memory and time for the HD reconstruction.
The HD frames frequency determines how many of the captured HD frames you are going to use for the HD reconstruction. For example, if you select 1/4, then only every fourth HD frame from the captured ones will be used to build the HD scan. The fewer HD frames you use, the fewer polygons the resulting scan will have (i.e., it will require less memory) and the less CPU time the processing will take. On the other hand, it is more likely that you will lose some of the scanned surface and the resulting HD scan will have holes. The HD frames frequency parameter is represented by the following values:
No HD frames
Every 8th frame
Every 4th frame
Every 2nd frame
Only HD frames
When scanning complex objects, shiny surfaces with insufficient data, or scanning at a high scanning speed, it is preferrable to use high HD frames frequency values: from 1/4 to 1. For simple objects with few details, we recommend choosing HD frames frequency with the 1/8 value.
Important
The HD reconstruction is a time-consuming and resource-intensive operation. On slow computers, it can take up to several hours. If Artec Studio evaluates your computer’s resources as insufficient for the selected values of the Point density and HD frames frequency parameters, then the corresponding warning will be displayed. For information on resources requirements, see the Using HD mode section in System Requirements.
To learn about additional options for adjusting the HD reconstruction, see HD Reconstruction in the Settings section.
See also
Disabling Distance Color¶
The Show distance color option (Figure 66) highlights the reconstructed surfaces in the field of view based on the working range of a particular scanner.
Red |
Surfaces are too close to the object. |
Orange, green |
Corresponds to the middle of range. Green represents the optimal distance. |
Blue |
Surfaces are too far away from the scanner and about to disappear. |
No color |
Surface is not being recorded. |
In some cases you may need to observe how well texture is being recorded. Disabling this feature would then help. Clear the Show distance color checkbox in the Scan panel to this end.
Real-time Processing¶
The Enable real-time processing option is ON by default. This option enables Artec Studio to perform real-time operations like saving, mapping textures and surface optimization, during the scan process. These simultaneously occuring operations may sometimes, depending on your system’s CPU model, significantly reduce the scanning speed (FPS). In order to optimize CPU usage and restore FPS during scanning, you can uncheck the Enable real-time processing option in the Scan panel.
Disabling real-time processing can prevent decline in scanning speed. The real-time operations are then automatically performed immediately after scanning.
Removing Redundant Frames¶
The Remove redundant frames option is ON by default. This setting removes redundant frames after scanning by analyzing the entire scan and deleting similar frames, even if they are not consecutive. It optimizes data and reduces unnecessary frame accumulation.
Tuning Texture Brightness¶
Note
This option is available only for Artec 3D scanners equipped with texture cameras.
You can adjust the Texture brightness setting in Preview mode. Use the slider to increase or decrease the brightness of frames captured by the color camera (see Figure 85). Note that the texture brightness affects texture quality as well as tracking steadiness. Observe the recommendations in the Table 3.
Surface Color |
Recommendation |
|---|---|
Dark or black |
Increase brightness |
Light-colored or white |
Decrease brightness |
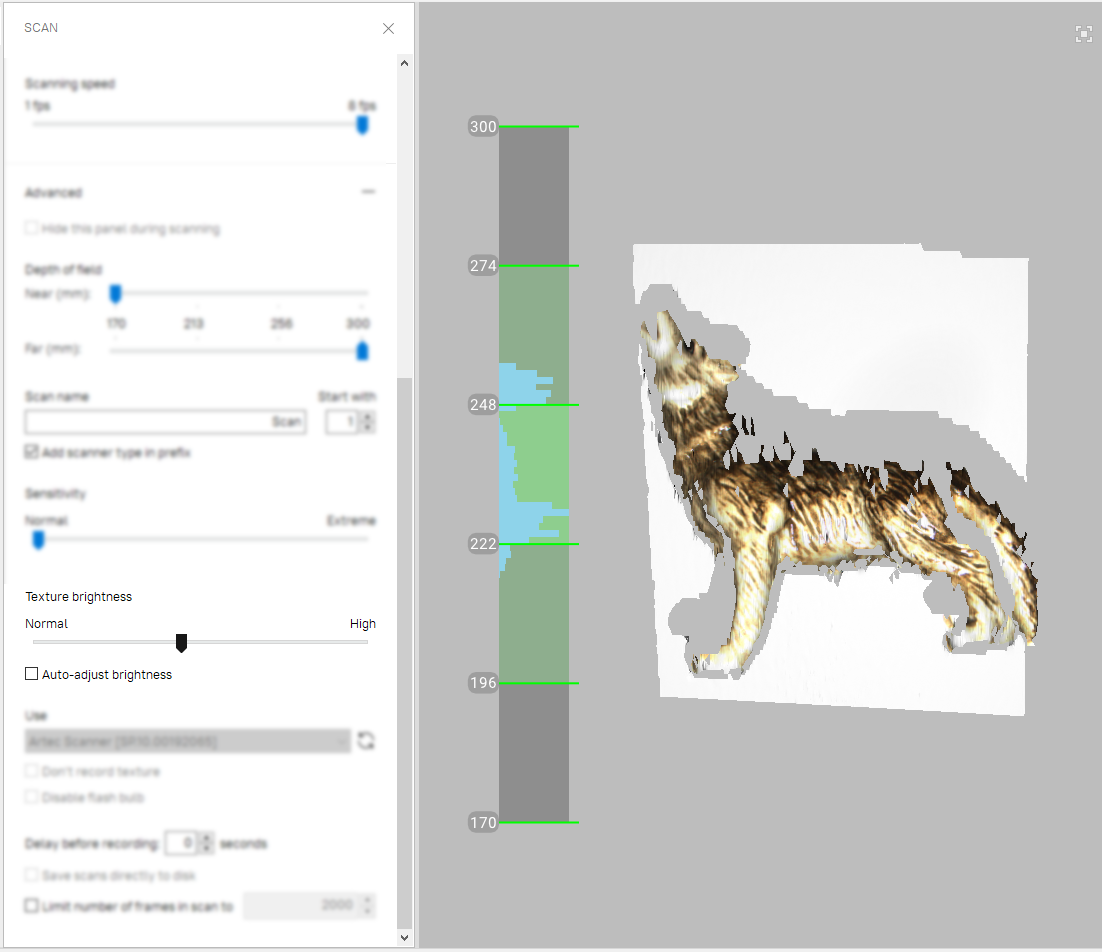
Figure 85 Increasing Texture brightness during Preview.¶
Preventing Overexposure¶
Artec Studio has error-proofing against overexposure. If the Auto-adjust brightness checkbox is selected and the specified value of Texture brightness causes texture to overexpose, the application will automatically decrease brightness to avoid damaging texture.
Overexposure Indicator¶
Artec Studio provides an indicator to highlight overexposed areas during scanning with Artec Spider II. If the Overexposure indicator checkbox is selected, the last frame will display areas that are too bright, helping users adjust the Geometry gain slider.
This feature is only useful when capturing submillimeter details and planning a fusion with a resolution of 0.09-0.05 mm. Consider the following recommendations:
If highlighted areas do not contain fine details, reducing Geometry gain is unnecessary—these scans remain valuable.
It is acceptable to scan an area of interest twice: first with higher Geometry gain and then with lower settings to ensure some frames have no overexposed regions.
The resolution remains optimal as long as at least one frame in the set is properly exposed.
The indicator visually represents point weights computed by the reconstructor. Points with lower weights (below 0.1) may appear in a warning color due to factors such as oversaturation or poor surface contrast.
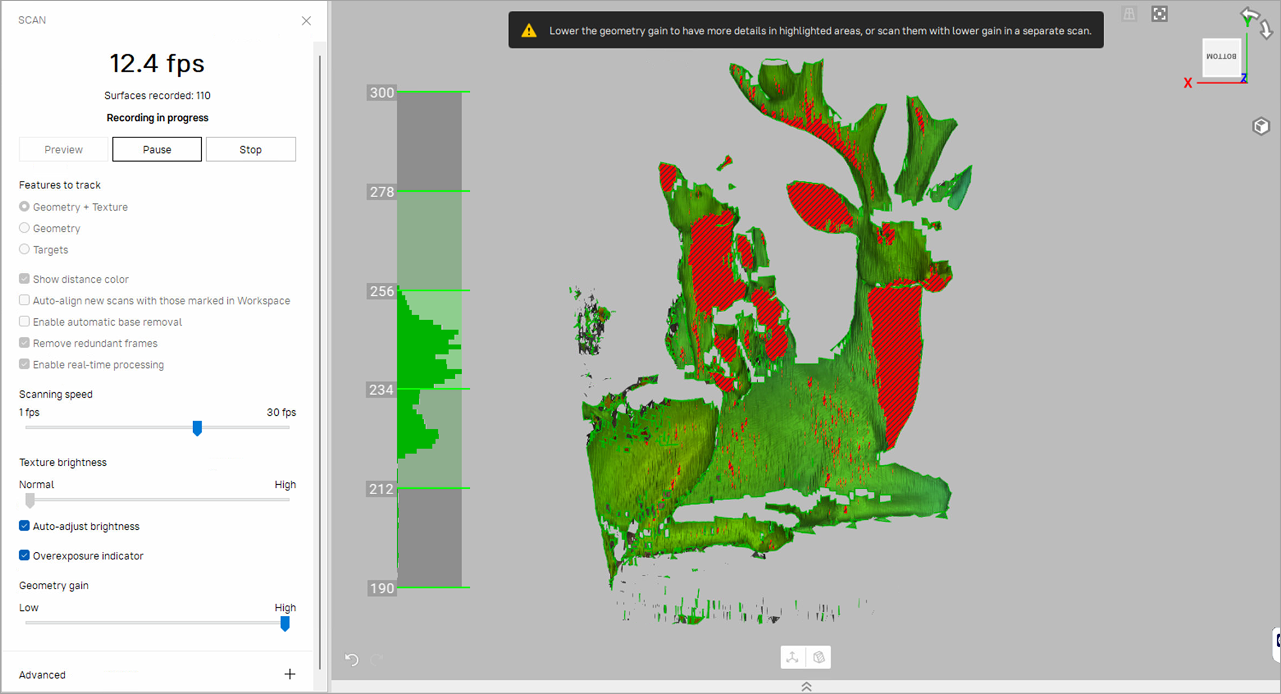
Figure 86 Overexposed areas highlighted in red¶
Sensitivity¶
You can tune the Sensitivity of Artec Spider scanner if the application fails to reconstruct particular surfaces. Increasing this setting enables the scanner to more easily capture black, reflective, translucent and fine objects (such as human hair). The higher the sensitivity, the noisier the recorded surfaces will be. Higher values may also reduce the scanning speed. For Eva and other Artec scanners, this setting is automatically adjusted.
Frequency for Capturing Texture Frames¶
By default, the Frequency of texture frames option is set to Automatic. In this mode, Artec Studio does not capture texture for every frame. To specify the frequency for capturing texture frames manually, do the following:
Check the One per … frame radio button (see Figure 84, right).
Using the spinner near it, specify the desired frequency: n.
After that, the texture will be captured for every n-th frame.
Deactivating Scanner Flash¶
If circumstances prohibit you from using the scanner flash, follow the directions below.

Figure 87 Influence of ambient light on captured results.¶
On left: flash is turned off; ambient light is poor; results—dark texture. On right: flash is turned off; lighting conditions are improved; results—good texture.
Note that if you disable the flash, you should compensate by using bright ambient light. According to our tests, acceptable texture quality is obtainable with the flash disabled if the surface illuminance is at least 1 000 lux. Compare the models shown in Figure 87, which were recorded under different lighting conditions.
The following procedure captures the textured model without using the scanner flash:
Open the Scan panel and click the Advanced link
Turn off the texture flash by selecting the Disable flash bulb checkbox
Use good illumination. Avoid fluorescent lamps.
Click Preview and direct the scanner at the object
Adjust Texture brightness and Texture exposure time. In most circumstances, values should be as low as possible, because increasing the brightness also increases a texture noise, whereas increasing exposure time can blur the texture. Instead of adjusting sliders, try to further improve the lighting conditions.
Capture the scene
Perform required postprocessing as described in Data Processing to get a textured model
Adjust texture parameters for this model as described in Texture Adjustment. Pay particular attention to the Hue and Saturation sliders. The Hue slider allows you to correct unwanted texture color.
Tuning Exposure Time¶
You can alter texture exposure time in the Preview mode. Adjust this parameter in tandem with the Texture brightness. Increasing exposure time can blur the texture. Don’t alter the default value unless it’s necessary.
Disabling Texture Recording¶
Select Don’t record texture checkbox if you don’t want to store texture information in your scans. It is located in the Advanced section of the panel and disengages both texture camera and texture flash in the scanner. Note that this option is unavailable for Artec Eva Lite. Don’t forget to select this checkbox once you have completed textureless scanning; otherwise, next time you want to start regular scanning the hybrid tracking mode could be unavailable.
Important
Just using the Geometry tracking mode it is still not sufficient for the application to don’t record texture. Make sure you clear the eponymous checkbox.
Decreasing Scanning Speed¶
Artec Eva captures objects at up to 16 frames per second, whereas Artec Spider at 7.5. Default values ensure comfortable scanning with smooth movements. However, if you find scanning speed inappropriate, you can decrease it. In this case, Artec Studio will record fewer identical frames and register them faster. To this end, use the Scanning speed slider in the Scan panel.
Important
Decreasing scanning speed may hinder scanning. Don’t use this slider unless it is absolutely necessary.
Limiting Number of Frames in Scans¶
Processing extra large scans might be problematic. To prevent Artec Studio from creating scans with an excessive number of frames, use the Limit number of frames in scan to counter. This counter defaults to 2000 frames in each scan.
Supplementary Settings¶
Scan Names and Starting Number¶
Customize scan names and starting number by entering your own values in the Scan name and Start with fields and changing the state of the Add scanner type in prefix checkbox. The software uses these values to create a scan title in the Workspace panel (see Figure 88, left). You can change the default values Eva Scan and 1 to, for example, Capture and 14.
Saving Scans to Disk¶
Trigger a capture mode that simultaneously records scanning results to a disk by selecting the Save scans directly to disk checkbox. This option is enabled when you’re working with an existing saved project (see Saving a Project) and can be useful when capturing large amounts of data on a computer with insufficient memory.
Delay Before Recording¶
Specify a delay (in seconds) before recording using the Delay before recording spinner under the Advanced section of the Scan panel. The countdown begins as soon as you click the Record button. To eliminate the delay, set the value to zero.
Depth of Field¶
Decrease specified operating-zone (Depth of field) by using the Near (mm) and Far (mm) sliders under the Advanced section of the Scan panel. Here you can only decrease range within the specified boundaries.
Motion Tolerance¶
As the name suggests, this option allows slight movement of the object without losing the scanner’s tracking. In other words, when this option is enabled, Artec Studio enables the scanners (Spider & Eva) to tolerate slight movements in the object being scanned. Motion tolerance is disabled by default, and can be enabled in the Advanced section of the Scan panel. This is particularly suitable for scanning moving objects like heads of children, objects with moving background or animals etc.
Specify Scanning Range¶
By default, Artec Studio provides the correct values for the minimum and maximum limits within which the cutoff planes are to be positioned. These values are different for each 3D scanner model, and they ensure that you capture good-quality 3D data. If high accuracy is a secondary concern, you can manually adjust the depth boundaries, allowing you to capture objects using an Artec L scanner or third-party 3D sensors positioned closer to or further from the object than is recommended. To do so, select the Override default depth range checkbox in the Settings dialog in the Scan tab, then specify new boundaries for the scanning range in millimeters (For more details about scan settings, see Capture).
Warning
Custom depth-range settings may reduce accuracy.
Hiding Scan Panel During Scanning¶
To widen the viewport during scanning, software automatically closes the Scan panel once you start recording using Artec Eva or Artec Spider scanners. The Hide this panel during scanning checkbox is located in the Advanced section and is cleared by default.
Temperature Compensation Wizard¶
To enable metrology precision for Eva, run a temperature compensation. It will adjust the scanner settings to the ambient temperature. In Advanced section, click Start temperature compensation wizard and wait for a process to finish.
Troubleshooting¶
Issue |
Possible Resolution |
|---|---|
Geometry + Texture radio button missing from Scan panel. |
You were probably scanning without texture. Clear the Don’t record texture checkbox in the Advanced section. |
Final model contains noticeable noise. |
You likely scanned the affected areas improperly, or the scanner was too far from the object. Rescan those areas. |
Tracking lost error persists. |
Make sure Scan using auto-alignment is enabled in the Settings dialog and use Geometry + Texture tracking. |